Comparative Chart of Simple Present and Present Continuous
3 Simple Present and Present Continuous
Simple Present and Present Continuous
Annapurna Madhuri
The present continuous or the present progressive tense is used to tell about whatever action is happening at the time of speaking.
Any temporary action, and/or an incomplete action is expressed in the present continuous tense. It is also known as present progressive tense.
The verb in the present continuous tense is made of two parts:
- The present tense form of verb 'to be' – is/am/are
- 'ing' affixed to the base verb.
Sentences in the present continuous form have a specified structure:
The affirmative sentence structure
subject + present tense form of verb 'to be' + base verb+ing
Example: She (subject)+ is (present tense form of 'to be')+ sing (base-verb)+ing ==> She is singing.
Negative sentence structure:
subject+ present tense form of verb 'to be' + not + base verb + 'ing'
Example: She is not singing
Interrogative structure:
Present tense form of verb 'to be' + subject + base verb + ing + Question tag
Example: Is she singing?
At the end of this lesson, all learners will be able to:
- Use the 'ing' form of verbs to describe actions as they happen.
- Use present continuous forms appropriately.
- Apply rules and exceptions to make a sentence in present continuous tense.
- Use present continuous tense in interrogative and negative sentences.
- Differentiate between the simple present and present continuous form of verbs.
Choose the correct form of verb in the following sentences:
Read the passage given below
At home on a Sunday.
It is a pleasant Sunday and my family and I are relaxing at home. My father usually washes his car on Sunday. But he is not washing the car now. He is watching news on the TV. My mother usually makes something special for lunch on Sundays. She is kneading the dough for making Aaloo-parathas for breakfast. My elder sister usually has her music class on Sundays. She is not singing now. She is helping mother in the kitchen. My brother usually helps father to wash the car. He is not helping father now. He is playing with Puppy, our pet dog. My friends generally come home on Sundays to spend their time with us. They are not coming now. They will come in the evening. I regularly clean my room on Sundays. I am not cleaning my room now. I am going to the market to bring some potatoes. My cat, Kitty is sleeping in her box now. My grandpa is reading the newspaper and grandm a is relaxing in the garden. Mr. Sharma is driving down to our house now. Father has invited him for the breakfast. My baby sister is smiling now. She has just had a cup of milk. Now I am telling this to you. How about you? What are you doing now?
Here we see things happening at the present moment. This is the present continuous tense. There is no information about the completion of the task. It started sometime in the near past and is still going on.
In the present continuous tense, each verb has two parts
1.Present tense form of verb 'to be' – is/am/are – known as helping verb
2.'ing' form of the base verb
Eg. She is singing.
Rules to make the 'ing' form of the verb:
- Add 'ing' to the base verb
- cry – crying
- play – playing
- say – saying
- go – going
- For verbs ending in 'e', remove the 'e' and add 'ing'
- come – coming
- live – living
- give – giving
- For verbs ending in 'l', add 'l' + 'ing'
- travel – travelling
- cancel – cancelling
- Other forms
- rub – rubbing
- mop – mopping
- lie – lying
- die – dying
Note: The verbs with 'ing' form are also known as Present Participle form of verbs.
We now know that present continuous tense is used to describe actions in the situations discussed in the picture below.
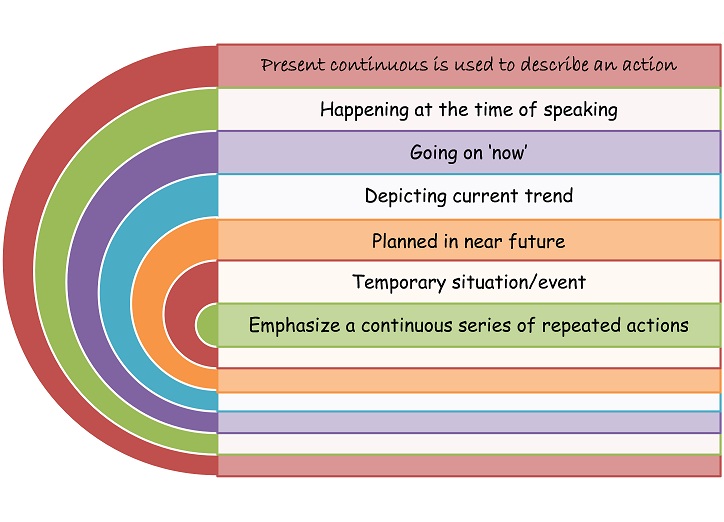
Signal words for present continuous tense:
- Actions happening at the time of speaking:
- at the moment, now, just now. right now, listen.., look..
- Actions going on now:
- at the moment, now
- Actions depicting current trend/taking place for a given time period/temporary situation:
- this week/this month/this year
- Actions planned in the near future:
- in the morning/afternoon/evening, at noon/night, tonight, tomorrow, next week/month/year/session
- Continuous series of repeated actions/development/changing situations:
- more and more
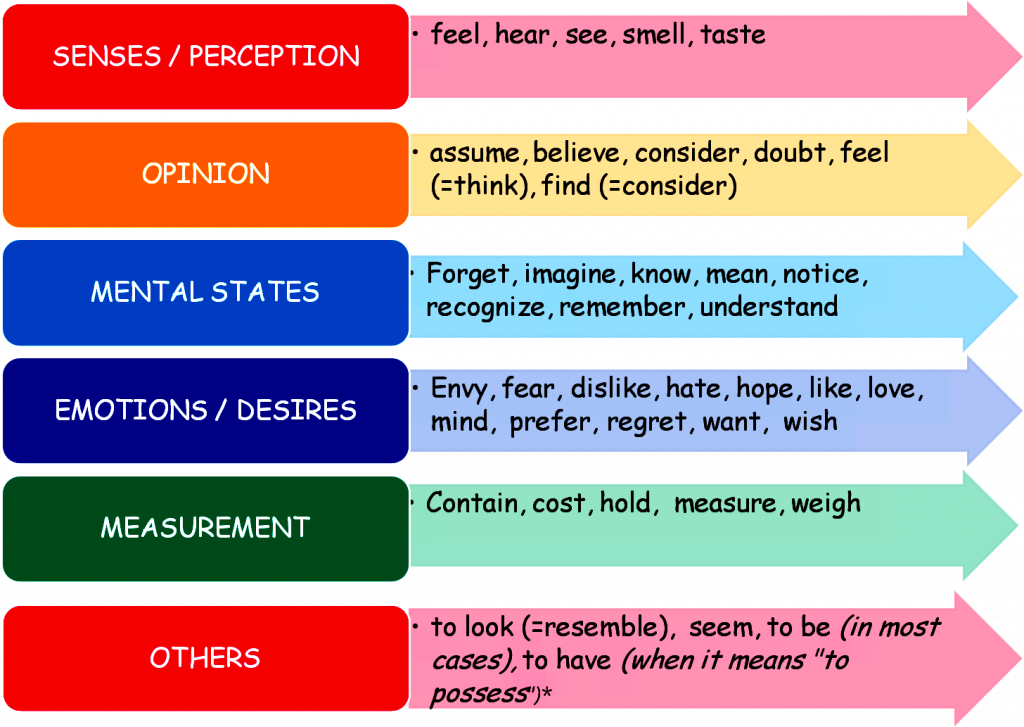
Non-Continuous verbs:
Some actions are used only in the simple present form, even if they are happening in any of the situations discussed above. This is when these are actions happening but we can't see somebody really doing it. Abstract verbs, possession verbs and emotion verbs are rarely used in the continuous tenses.
Interrogative and Negative sentences in present continuous tense.
Simple present Vs. present continuous
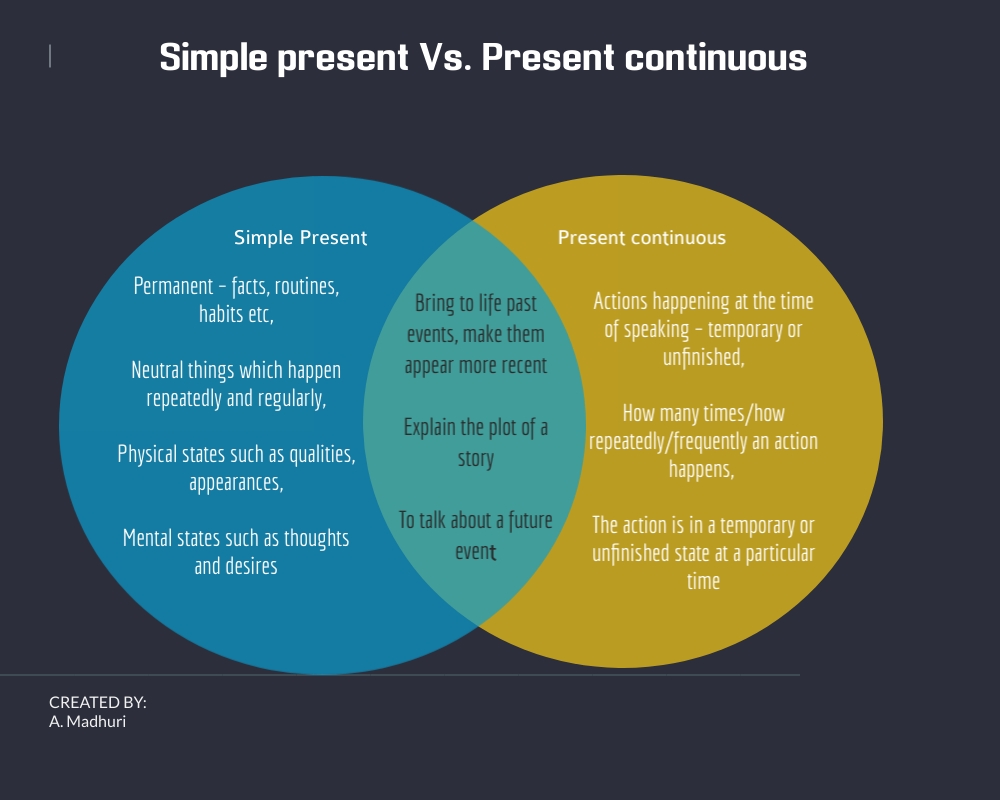
| Basis of differences | SImple Present Tense | Present Continuous Tense |
| Basic | Talk about things we see as permanent, that always hold true: facts, routines, habits and so on | Talk about things that are happening at the time of speaking – temporary or unfinished |
| Repeated actions | Talk about neutral things that happen regularly or repeatedly | Talk about how often things happen |
| States | Talk about physical states such as appearances, qualities and possession and about mental states such as thoughts and desires | Show that something at that particular moment is temporary or yet to be complete. |
Similarities:
Both Simple present and present continuous tenses are used to
- Bring to life any events of the past and speak of it as if it is happening here and now.
- Explain the plot of a story
- Talk about the future.
shielsmomentown1959.blogspot.com
Source: https://kpu.pressbooks.pub/effectiveenglish/chapter/simple-present-and-present-continuous/
0 Response to "Comparative Chart of Simple Present and Present Continuous"
Post a Comment